
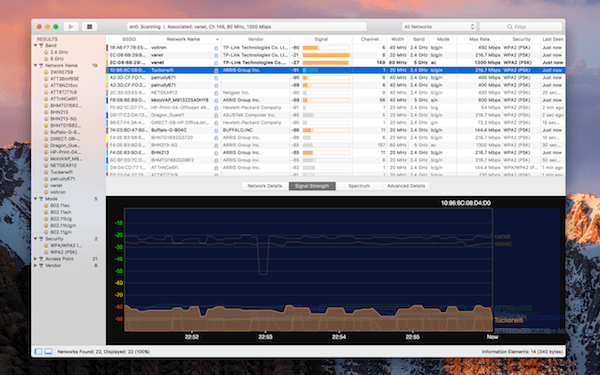
In these, the more negative the number is, the smaller its signal is. If the signal is greater than one milliwatt, the dBm measurement will be positive, and if the signal is less than one milliwatt, then the ratio will be negative (logarithms of values between 0 and 1 are negative).įor most Wi-Fi networks, you will see the signal measurement be between around -10 and -70 dBm, and should see the noise between -80 to -100 dBm. This may seem odd, but is correct because the measurement of the wireless signal in watts is converted to a logarithmic ratio unit called dBm, which is the ratio of the measured signal to one milliwatt of power. In the tool you can monitor the Wi-Fi performance, and see the graphed signal and noise power levels, which in most cases will be negative numbers. Moving a computer near the router will give a much higher signal-to-noise ratio by increasing the received signal strength, even though the noise does not change.
#Check for wifi interference mac mac
On Mac systems running OS X Lion, Apple has included a program called Wi-Fi Diagnostics Utility (available in the /System/Library/CoreServices/ folder) that can do this, but if you have other versions of OS X, then you can use a third-party tool such as APGrapher, AirRadar, iStumbler, or Kismac. The Wi-Fi receiver on your computer is constantly measuring both the desired signal strength and the noise signal strength, and if you are experiencing connectivity problems, you can use a tool that will display these measurements for you. Therefore, to determine the Wi-Fi signal quality you need to be able to compare the data and noise signals that your computer's radio is picking up. These examples deal with audio, but Wi-Fi waves work in a similar manner, where background noise can result in the inability for the computer to understand the desired signal, especially when the signal is weak. In this case either the desired signal is too weak, or the noise signals are too strong and the radio cannot filter them out or otherwise manage them, resulting you hearing a garbled mess. If you are listening to music over the radio, then static and interference from other radio waves can at times be so great that you cannot make sense of the desired audio signal from the noise. When you play music (a desired signal), this background noise is usually drowned out because the signal for the music is far greater than the unwanted noise signals however, this is not always the case. In addition to this noise, you may hear a humming or buzzing sound, which is interference from other electrical devices that is being picked up by the player's electronics. This innate noise in the signal comes from the quality of the electronics in the player itself. For example, if you turn on a cheap stereo player and crank up the volume without playing anything, you will likely hear a bit of static "white noise" in the background. In all analog connections you have a certain amount of unwanted signal called "noise," which is a combination of interference from other electrical devices and the innate "fuzziness" of the output. The quality for any analog signal, be it electrical, optical, or radio, can be determined by comparing the desired signal level to the background noise level in the signal in what's known as a signal-to-noise ratio. When Wi-Fi drop-outs happen, you may see one of these symbols in the OS X menu bar.

Besides the system configuration, an cause for Wi-Fi drop-outs can also be poor Wi-Fi signal quality. Recently I covered a number of approaches to fixing Wi-Fi dropout problems, though these only covered the configuration options in the router and the computer itself. For the most part Wi-Fi technology works quite well to keep your Mac, iPhone, and other devices connected however, there are times when certain devices or setups may be plagued with Wi-Fi dropouts.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
